Table of Contents
Summarize and analyze this article with
Introduction
As banks scale AI across compliance, fraud, risk, and customer operations, the need for strong AI Governance in Banking has become non-negotiable. Regulatory pressure is rising, data-use rules are tightening, and autonomous decision systems demand oversight. By 2025, more than 78% of global banks had embedded AI in at least one core workflow, while 60% adopted multi-function AI deployments spanning credit scoring, AML, KYC, and customer risk evaluation.
In 2026, analysts expect banks to increase AI governance spending by 22% to meet evolving compliance mandates. This rapid adoption brings both opportunity and responsibility. Fairness, privacy, transparency, explainability, and operational safety now define the future of AI-enabled banking. The real challenge is finding a way to innovate confidently while still showing regulators that every AI decision is safe, fair, and fully compliant.
This blog explores key challenges, governance gaps, and actionable solutions banks need today.
Why AI Governance Matters Now
-
In 2025, 89% of banks used AI for real-time compliance monitoring , improving anomaly detection speed by 40%.
- Banks using AI for compliance saw a 15% drop in audit findings and 19% reduction in compliance costs.
- GenAI adoption remains immature while only 5% to 10% of banks have production-grade governance programs.
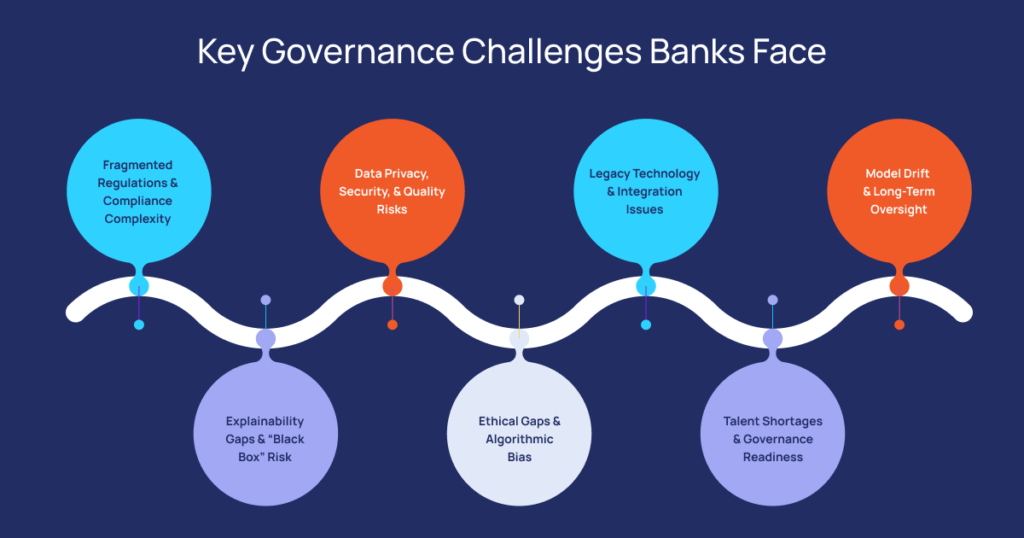
Key Governance Challenges Banks Face
1. Fragmented Regulations and Compliance Complexity
2. Explainability Gaps and “Black Box” Risk
3. Data Privacy, Security, and Quality Risks
4. Ethical Gaps and Algorithmic Bias
5. Legacy Technology and Integration Issues
6. Talent Shortages and Governance Readiness
7. Model Drift and Long-Term Oversight
Actionable Solutions for Stronger AI Governance
1. Build Cross-Functional Governance Structures
- human-in-the-loop controls
- an AI oversight board
- documented responsibility chains
- escalation and approval workflows
2. Adopt Explainable AI to Strengthen Transparency
3. Strengthen Data Governance, Privacy, and Security
- privacy-by-design
- zero-trust architectures
- encryption and anonymization
- lineage tracking
- controlled access rights
- automated breach detection
4. Implement Bias Detection and Ethical Controls
5. Enable Full Lifecycle AI Governance
- pre-deployment testing
- model approvals
- continuous drift detection
- version control
- periodic retraining
- performance documentation
6. Build AI Skills and Training Programs
7. Manage Third-Party and Vendor Risk
- vendor transparency
- contractual audit rights
- shared responsibility models
- third-party compliance certifications

Expected Outcomes of Strong AI Governance
- improved regulatory compliance
- increased transparency in AI models
- reduced audit findings
- enhanced privacy protection
- more reliable operations
- stronger customer trust
- long-term, ethical AI scalability
Proposed AI Governance Blueprint for Banks
| Component | Key Actions |
|---|---|
| Governance Structure | Create an AI Oversight Committee; assign clear accountability; include legal, risk, compliance, IT, and business leadership. |
| Explainability & Transparency | Use XAI for decision-making models; build audit trails; record decision logic for credit, fraud, and risk. |
| Data Governance & Privacy | Enforce data quality and lineage; apply anonymization where needed; manage consent; ensure strong encryption and secure storage. |
| Ethical & Bias Controls | Audit for bias regularly; diversify training data; define fairness metrics; monitor for disparate impact. |
| Lifecycle Management | Implement version control; enable continuous monitoring; perform periodic retraining or recalibration; decommission obsolete models. |
| Talent & Training | Build specialized teams; conduct regular cross-functional training; enable continuous upskilling. |
| Integration & Scale | Prioritize integration with legacy systems; treat AI as an enterprise function, not a point solution; scale progressively with compliance in mind. |
Conclusion
AI can transform everything from compliance to fraud detection, but without strong governance, the risks are significant. When banks build a solid governance framework that is grounded in ethics, data discipline, explainability, and accountability, they unlock AI’s full value while safeguarding customers and their own reputation.
Pitech helps financial institutions design compliant, scalable, ethical AI systems. By aligning governance with transparency, privacy, fairness, and accountability principles, PitechSol enables banks to innovate responsibly while reducing legal risk.
Key Takeaways
-
AI Governance in Banking is essential as regulations tighten and AI adoption accelerates.
- Key risks include bias, privacy issues, black-box models, and inconsistent regulatory expectations.
- Explainable AI and strong compliance practices build trust and meet audit requirements.
- Robust data governance and privacy-by-design protect sensitive financial information.
-
End-to-end lifecycle oversight strengthens AI Risk Management Finance .
- Cross-functional governance teams ensure responsible innovation and sustained customer trust.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do banks ensure AI-driven decisions are fair and unbiased?
By auditing datasets, applying fairness metrics, validating model behavior, and continuously monitoring for drift or disparate impact.
What are the biggest challenges in AI governance for financial institutions?
Regulation ambiguity, explainability gaps, data privacy risks, vendor dependency, bias, and limited internal AI governance talent.
How does AI governance help banks comply with regulations like the EU AI Act?
It ensures transparency, documentation, human oversight, risk assessments, and lifecycle monitoring—requirements mandated under high-risk AI categories.
What frameworks are best for managing AI risks in banking?
How can banks implement explainable AI models effectively?
Adopt XAI tools, integrate decision-explanation logs, require interpretability for all high-risk use cases, and document rationale for credit, fraud, and AML decisions.
What role does human oversight play in autonomous AI banking systems?
It ensures accountability, prevents over-automation, and enables intervention when AI behavior becomes risky or non-compliant.
How do financial institutions protect customer data in AI applications?
Through encryption, anonymization, privacy-by-design architecture, access controls, and continuous monitoring for threats.
What are the operational risks of deploying AI in banking?
Model drift, data quality gaps, integration failures, vendor opacity, system errors, and non-compliant autonomous decisions.
How do banks manage vendor risks related to AI solutions?
Through transparency requirements, compliance certifications, third-party audits, contractual controls, and continuous performance monitoring.





