Table of Contents
Summarize and analyze this article with
Cybercrime has become one of the biggest threats to financial stability and trust. According to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center, cybercrime has surged into a $16 billion crisis, with a cyberattack occurring every 39 seconds, translating to nearly 2.2 million attacks every day. For banks, insurers, and other regulated sectors, the stakes are even higher. A single breach can lead to massive financial losses, compliance penalties, and reputational damage that takes years to rebuild.
As our digital ecosystems stretch across cloud services, mobile networks, and the evolving world of open banking, protecting data and ensuring systems stay resilient has become a necessity. This guide outlines practical, actionable strategies to help financial leaders strengthen defenses, reduce cyber risk, and build a safer, more resilient digital future.
What Is Cybercrime? Understanding Modern Digital Threats
Cybercrime encompasses any illegal activity conducted through internet-connected devices or computer networks. These malicious activities range from identity theft and financial fraud to data breaches and online harassment, with cybercriminals exploiting both technological vulnerabilities and human psychology.
Most Common Types of Cybercrime You Need to Know
1. Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Phishing remains the most prevalent form of cybercrime, where attackers impersonate legitimate organizations to steal credentials or sensitive information. These attacks typically arrive via email, text message, or social media, using urgent language and deceptive links to manipulate victims.
Warning Signs:
- Generic greetings like "Dear Customer"
- Urgent threats demanding immediate action
- Suspicious sender email addresses
- Shortened or disguised URLs
- Requests for sensitive information
2. Identity Theft and Financial Fraud
Identity theft occurs when criminals steal your personal information to access financial accounts, open credit lines, or commit crimes in your name. This information is often obtained through data breaches, phishing scams, or dark web purchases.
3. Malware and Ransomware
Malicious software infiltrates devices to steal data, monitor activity, or encrypt files for ransom. Common types include:
- Viruses: Self-replicating programs that damage systems
- Trojans: Disguised malware that appears legitimate
- Ransomware: Encryption-based extortion software
- Spyware: Covert monitoring applications
- Adware: Unwanted advertising software
4. Data Breaches
Data breaches expose confidential information held by businesses and organizations, often resulting in millions of records being compromised. Your personal data may then be sold on the dark web, leading to secondary crimes like identity theft.
5. Online Harassment and Cyberstalking
Digital platforms enable harassment through cyberbullying, stalking, doxing, and persistent abuse. This form of cybercrime causes psychological harm and can escalate to real-world threats.
6. Business Email Compromise (BEC)
BEC attacks target organizations by impersonating executives or trusted vendors to authorize fraudulent wire transfers or sensitive data disclosure.
How to Prevent Cybercrime: 15 Essential Protection Strategies
Strong Authentication Practices
1. Implement Strong Password Hygiene
Create unique passwords for every account using these guidelines:
- Minimum 15 characters combining uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols
- Avoid personal information like birthdays, names, or common words.
- Never reuse passwords across multiple accounts.
- Use a reputable password manager to securely store credentials.
2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication adds a critical security layer by requiring two or more verification methods. Enable MFA on all accounts that offer it, prioritizing:
- Banking and financial services
- Email accounts
- Social media platforms
- Cloud storage services
- Work-related applications
Software and Device Security
3. Maintain Current Software Updates
Cybercriminals exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software. CISA recommends establishing a routine to update:
- Operating systems (Windows, macOS, iOS, Android)
- Web browsers and browser extensions
- Antivirus and security software
- Mobile applications
- Router firmware
4. Install Comprehensive Security Software
Deploy robust cybersecurity solutions that provide:
- Real-time threat detection and removal
- AI-powered scam detection
- Firewall protection
- Web protection and safe browsing tools
- Automatic security updates
5. Secure Your Home Network
Transform your home network into a fortress:
- Replace default router passwords with strong, unique credentials.
- Enable WPA3 encryption (or WPA2 if WPA3 is unavailable)
- Create a separate guest network for visitors.
- Disable remote management features
- Regularly update router firmware.
- Consider using a VPN for encrypted internet traffic.
Safe Online Behavior
6. Practice Cautious Link and Attachment Handling
Before clicking any link:
- Hover over links to preview the actual destination URL
- Verify sender authenticity through independent channels.
- Be skeptical of urgent or threatening messages
- Avoid downloading attachments from unknown sources
- Use link-checking services for suspicious URLs
7. Manage Your Digital Footprint
Minimize your online exposure:
- Review and restrict social media privacy settings
- Limit publicly visible personal information
- Remove unused online accounts
- Avoid oversharing details about your location, schedule, or family
- Use privacy-focused search engines and browsers
8. Protect Personal Information
Guard sensitive data zealously:nimize your online exposure:
- Never share Social Security numbers unnecessarily
- Provide minimal information on online forms
- Use temporary email addresses for non-essential registrations
- Shred physical documents containing personal data
- Be cautious about public Wi-Fi usage for sensitive transactions
Financial Protection Measures
9. Monitor Financial Accounts Regularly
Establish a routine financial review process:
- Check bank statements weekly for unauthorized transactions
- Review credit card activity after each billing cycle
- Set up transaction alerts for unusual activity
- Monitor credit reports from all three major bureaus
- Consider credit monitoring services for real-time alerts
10. Respond Swiftly to Data Breaches
When notified of a data breach:
- Immediately change passwords for affected accounts
- Enable multi-factor authentication if not already active
- Place fraud alerts on your credit reports
- Monitor accounts closely for suspicious activity
- Consider identity theft protection services
Advanced Protection Strategies
11. Use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
VPNs encrypt your internet connection, protecting data from interception:
- Essential when using public Wi-Fi networks
- Masks your IP address and location
- Prevents ISP tracking of browsing activity
- Enables secure remote work connections
- Consider identity theft protection services
12. Implement Email Security Best Practices
- Use separate email addresses for financial accounts, shopping, and social media
- Enable email filtering and spam protection
- Be wary of spoofed sender addresses
- Verify unexpected requests through alternative communication channels
- Use encrypted email services for sensitive communications
13. Practice Safe Mobile Device Usage
Mobile devices require special attention:
- Download apps only from official stores
- Review app permissions before installation
- Disable unnecessary location services
- Use device encryption features
- Enable remote wipe capabilities
- Avoid jailbreaking or rooting devices
- Backup Critical Data Regularly
Protect against ransomware and data loss:
- Follow the 3-2-1 backup rule (3 copies, 2 different media types, 1 offsite)
- Use encrypted backup solutions
- Test backup restoration periodically
- Keep backups disconnected from main networks
- Consider cloud-based backup services
15. Stay Informed About Emerging Threats
Cybersecurity requires ongoing vigilance:
- Follow reputable cybersecurity news sources
- Subscribe to security alerts from relevant organizations
- Participate in security awareness training
- Review and update security practices quarterly
- Share knowledge with family and colleagues
Emerging Cybercrime Trends to Watch
Staying ahead of cybercriminals requires awareness of evolving tactics and technologies.
AI-Powered Attacks
Artificial intelligence enables more sophisticated attacks:
- Deepfake technology is creating convincing impersonations
- AI-generated phishing emails with perfect grammar and context
- Automated vulnerability scanning and exploitation
- Machine learning-based social engineering
Internet of Things (IoT) Vulnerabilities
The rise of connected devices has opened up entirely new avenues for cyber threats, with projections suggesting there could be more than 75 billion IoT devices in use by 2025.
- Smart home device exploitation
- Compromised security cameras and baby monitors
- Vulnerable medical devices
- Automotive system hacking
- Industrial control system attacks
Cryptocurrency-Related Crimes
Digital currency presents new opportunities for criminals, with crypto-related fraud exceeding $5.6 billion in recent years:
- Cryptocurrency theft from wallets and exchanges
- Ransomware demanding cryptocurrency payments
- Investment scams promising unrealistic returns
- Cryptojacking (unauthorized cryptocurrency mining)
Supply Chain Attacks
Criminals target vendors to reach ultimate victims:
- Compromised software updates
- Infected third-party components
- Vendor email compromises
- Cloud service provider breaches
Mobile-First Attacks
Smartphones become primary targets, with mobile banking trojans increasing by 50%:
- Banking Trojan applications
- SMS phishing (smishing)
- Malicious apps in official stores
- SIM swapping attacks
- Mobile payment fraud
Building a Stronger, Safer Bank — From Core Systems to Cloud
As financial networks grow increasingly interconnected, regional and mid-tier banks face heightened threats from cybercriminals targeting their core infrastructure, digital platforms, and customer data. Consequently, cyber resilience has evolved into a fundamental requirement for institutions advancing their digital initiatives.
Evolving Threats in Modern Banking
Banking institutions have become high-value targets due to the convergence of legacy systems, open banking APIs, and distributed digital ecosystems. Key challenges include:
- Account Takeover & Payment Fraud: Credential stuffing and session hijacking, exploiting outdated authentication mechanisms.
- Wire & Transfer Manipulation: Business Email Compromise (BEC) and synthetic identity fraud are driving multi-million-dollar losses.
- Insider Threats & Privilege Abuse: Gaps in identity governance allowing unauthorized access to sensitive systems.
- Third-Party & API Exploits: Integration risks in fintech collaborations and open banking environments.
- Mobile & Endpoint Malware: Rapid growth of banking trojans targeting executive and staff devices.
Strategic Security Priorities for Banking Leaders
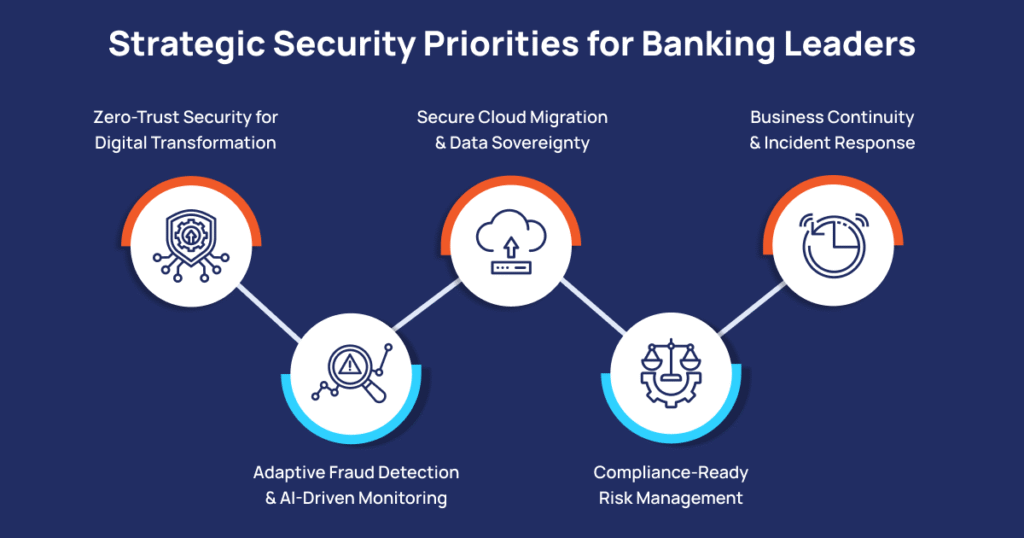
1. Zero-Trust Security for Digital Transformation
Implement a Zero-Trust framework across core, digital, and cloud environments. PiTech helps banks enforce identity-centric access controls, continuous authentication, and micro-segmentation to prevent lateral movement within networks.
2. Adaptive Fraud Detection and AI-Driven Monitoring
Use AI and behavioral analytics to detect anomalies in real time. Our solutions enable early identification of payment fraud, insider threats, and unauthorized system activities before they escalate into financial losses.
3. Secure Cloud Migration and Data Sovereignty
As banks migrate workloads to hybrid and multi-cloud models, PiTech ensures compliance with RBI, GDPR, and ISO-27001 standards while maintaining full data sovereignty and encryption across environments.
4. Compliance-Ready Risk Management
Automate audit trails, reporting, and compliance workflows to align with evolving regulatory frameworks such as PCI-DSS, FFIEC, and SOC 2. PiTech’s integrated risk dashboards provide leadership with continuous oversight of vulnerabilities and incidents.
5. Business Continuity and Incident Response
Implement real-time backup, disaster recovery, and automated incident response playbooks. Our frameworks ensure operational resilience even in the face of ransomware or system outages.
Cybersecurity Framework for Banks to Reduce Cyber Risk
A robust cybersecurity framework is essential for banks to protect digital assets, ensure compliance, and uphold customer trust. The following pillars define a comprehensive security approach that strengthens every layer of defense, from identity management to regulatory compliance.
| Focus Area | Objective | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Identity & Access Management | Eliminate unauthorized entry points | AI-based identity governance and adaptive MFA |
| Payment Security | Prevent fraud and data leakage | Real-time transaction monitoring & SWIFT security controls |
| Cloud & API Security | Protect interconnected systems | API gateways, tokenization, and encrypted communication |
| Data Governance | Safeguard sensitive assets | Data loss prevention, encryption, and secure key management |
| Endpoint Security | Secure branch and staff devices | EDR/XDR integrated monitoring and remote management |
| Compliance & Reporting | Ensure regulatory alignment | Automated policy management and compliance dashboards |
Conclusion
Cybercrime continues evolving in sophistication and scale, but implementing comprehensive security practices can significantly reduce their vulnerability. Protection requires ongoing vigilance, combining robust technical defenses with smart digital behavior.
Whether protecting yourself, or your organization, the investment in cybersecurity pays dividends through prevented losses, protected privacy, and peace of mind. Begin implementing these strategies today to secure your digital life against tomorrow’s threats.
Remember that cybersecurity is not a one-time effort but an ongoing commitment. Stay informed, remain vigilant, and don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance when needed. Your digital safety depends on the actions you take today.
Drive Secure Transformation with PiTech
Whether you’re consolidating systems post-merger, launching digital banking platforms, or migrating to the cloud, PiTech delivers the architecture, intelligence, and resilience your bank or organization needs to stay ahead of threats while accelerating innovation.
Contact PiTech Solutions to learn how we can help secure your organization against evolving cyber threats.
Key Takeaways
- Cybercrime is rising fast, with attacks happening every few seconds and costing billions worldwide.
- Financial institutions face serious risks, including heavy losses, penalties, and damaged trust.
- Cyber resilience is now a basic requirement for digital banking and financial operations.
- The most common cybercrimes are phishing, identity theft, ransomware, data breaches, and email scams.
- Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication are essential for protecting accounts.
- Keeping software updated and securing devices helps block known vulnerabilities.
- Safe online habits, such as checking links and limiting personal information, reduce exposure.
- Regularly monitoring financial accounts helps catch fraud early and limit damage.
- New threats are emerging through AI tools, connected devices, cryptocurrency, and mobile apps.
- Banks should focus on zero-trust security, AI-based fraud detection, secure cloud systems, and strong compliance measures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the most common cybercrimes today?
The most frequent types of attacks include phishing, identity theft, ransomware, data breaches, and business email compromise. Criminals often take advantage of weak passwords, outdated systems, or human mistakes to access sensitive data.
How can individuals and businesses prevent cyberattacks?
Create strong and unique passwords, enable multi factor authentication, keep your software updated, and avoid clicking on suspicious links. Businesses should use zero-trust frameworks, advanced threat detection powered by artificial intelligence, and conduct regular security audits.
Why is cybersecurity important for banks and financial institutions?
Banks are prime targets because they hold valuable data and handle critical financial operations. A strong cybersecurity foundation helps maintain customer trust, meet regulatory standards, and prevent financial losses or data breaches.
What should I do if my data or bank account is compromised?
Change your passwords right away, contact your bank or IT support team, and set up fraud alerts. Report the incident to the authorities and closely monitor all your financial accounts for any unusual activity.
How does PiTech Solutions help organizations stay secure?
PiTech provides complete cybersecurity support that includes zero trust implementation, artificial intelligence-driven fraud detection, compliance management, and defense-grade secure cloud transformation. These solutions help organizations build a strong and resilient digital environment.





