Table of Contents
Summarize and analyze this article with
Introduction
Why Security and Compliance Matter in Banking AI Integration Services
When banks adopt AI integration services, several distinct factors emphasize the importance of security and compliance:
- Sensitive data handling & exposure: Banking AI projects often process large volumes of personal and financial data, such as customer account details, transaction history, and credit profiles. This creates a heightened risk of data leakage or misuse
-
Regulatory obligations: The banking industry is tightly regulated. When AI systems are deployed, they must adhere to regulations governing data privacy (GLBA, CCPA), banking compliance, anti-money laundering (AML), Know Your Customer (KYC), and emerging AI governance frameworks.
- Impact of Model decisions: In banking, AI might affect loan approvals, credit scoring, and fraud decisions—outcomes that carry legal, ethical, and reputational weight. Thus, explainability, fairness, and auditability are very critical.
- Operational integration & vendor risk: Many banks rely on third-party vendors for AI integration services. That introduces supply-chain risk, hidden dependencies, and increased complexity of oversight.
Key Pain-Points for AI Integration in Banking
Here are common pain points banks and AI integration service providers face:
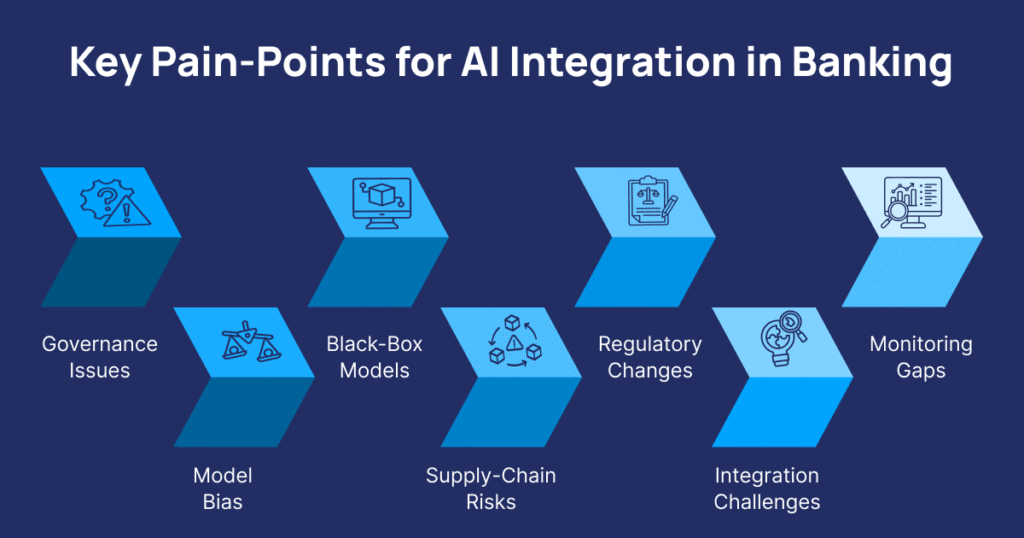
- Lack of governance clarity and accountability
- Model bias and fairness issues
- Opaque, “black-box” models such as LLM integration systems
-
Evolving regulations and security compliance AI requirements
- Integration with legacy systems and IT system integration challenges
- Weak operational monitoring and governance gaps
Strategic Framework for Secure & Compliant AI Integration in Banking
Here is a structured framework that banks and their service providers can adopt to embed security and compliance in AI integration services.
1. Governance & Compliance Foundation
- Establish an AI governance committee covering risk, compliance, security, and business teams.
- Define policies for data lifecycle, AI agent integration, vendor management, and model accountability.
- Align with frameworks like ISO 42001 and NIST AI RMF.
With this kind of strong foundation, banks can have a truly enterprise-wide AI integration.
2. Secure Architecture & Zero-Trust Integration
- Adopt zero-trust principles across infrastructure.
- Use DevOps AI practices for secure model deployment.
- Encrypt data, tokenize sensitive information, and validate vendors.
- Ensure third-party systems align with enterprise AI solutions and compliance needs.
Effective governance does not slow innovation, but it provides structure and trust, enabling safe scaling of AI solutions across divisions.
3. Data Lifecycle & Model Integrity
- Classify data by sensitivity. Maintain audit trails and data lineage.
- Adopt AI automation tools for model versioning, anomaly detection, and compliance alerts.
- Ensure protection against adversarial threats and drift.
4. Explainability, Monitoring & Auditability
- Use Explainable AI frameworks to make decisions traceable.
- Enable dashboards that track bias, drift, and model health.
- Maintain transparency and continuous data analytics integration for performance audits.
5. Vendor & Supply-Chain Risk Management
- Screen vendors for compliance readiness and transparency.
- Use contracts to ensure they meet the bank's governance and AI integration automation standards.
- Regularly audit enterprise AI integration platforms and maintain a secure software bill of materials.
6. Incident Response, Compliance & Continuous Improvement
- Implement AI-centric incident response processes.
- Conduct periodic security reviews and vendor audits.
- Integrate new regulations into your AI service modernization cycle.
- Encourage a compliance-by-design culture throughout the organization.
Apply the Framework for AI Integration Services in Banking
When a bank engages an AI integration services provider for use cases such as fraud detection, AML compliance, or customer onboarding, the delivery process must follow a structured and secure framework.
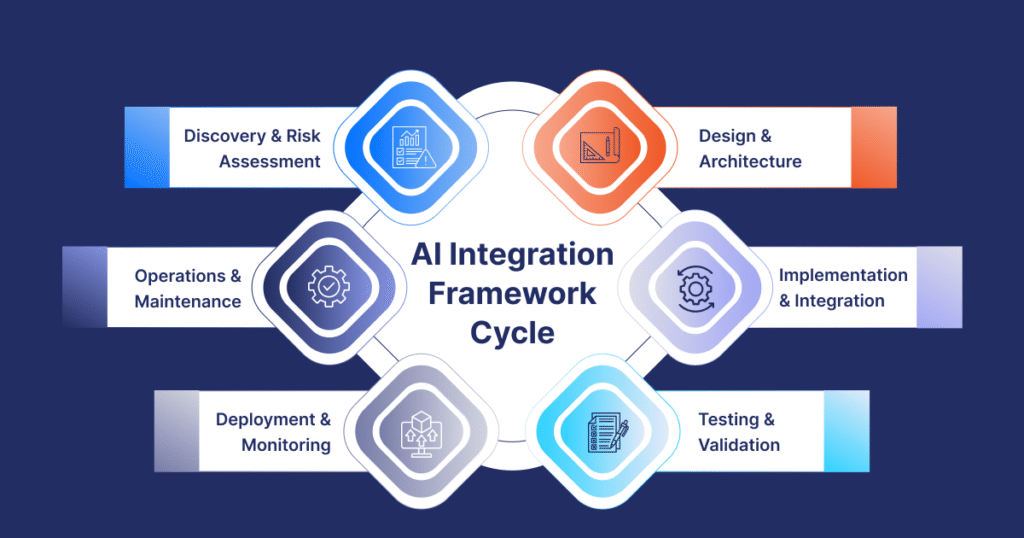
1. Discovery & Risk Assessment
- Identify the use case, assess data and model requirements, and evaluate regulatory exposures.
- Define the integration scope, including setup type (on-premises, cloud, or hybrid), including AI workflow integration and vendor controls.
- Perform a comprehensive risk assessment to address data, compliance, and operational risks.
2. Design & Architecture
- Design a secure architecture covering data storage, processing, encryption, and access management.
- Enable audit logging, model versioning, and transparency for regulatory review.
- Align the design with enterprise architecture, cybersecurity, and compliance frameworks.
3. Implementation & Integration
- Apply secure coding practices, including input validation, endpoint protection, and sandboxing.
- Integrate seamlessly with legacy systems using advanced IT system integration strategies while isolating sensitive data and high-risk modules.
- Prepare and validate data through anonymisation and fairness testing before model deployment.
4. Testing & Validation
- Conduct functional, adversarial, and penetration testing to ensure system security and reliability.
- Run bias and fairness audits to maintain model integrity and compliance.
- Validate explainability and traceability to support transparent decision-making.
5. Deployment & Monitoring
- Deploy models using controlled versioning, rollout, and rollback mechanisms.
- Continuously monitor live data, model behaviour, and drift patterns.
- Maintain audit trails and compliance dashboards to ensure accountability and regulatory assurance.
6. Operations & Maintenance
- Retrain and recalibrate models periodically to maintain accuracy and relevance by updating LLM-powered IT services.
- Apply vendor updates and security patches as part of ongoing maintenance.
- Conduct regular vendor assessments and third-party audits, updating contracts where required.
- Monitor model outcomes through AI-driven process improvement mechanisms
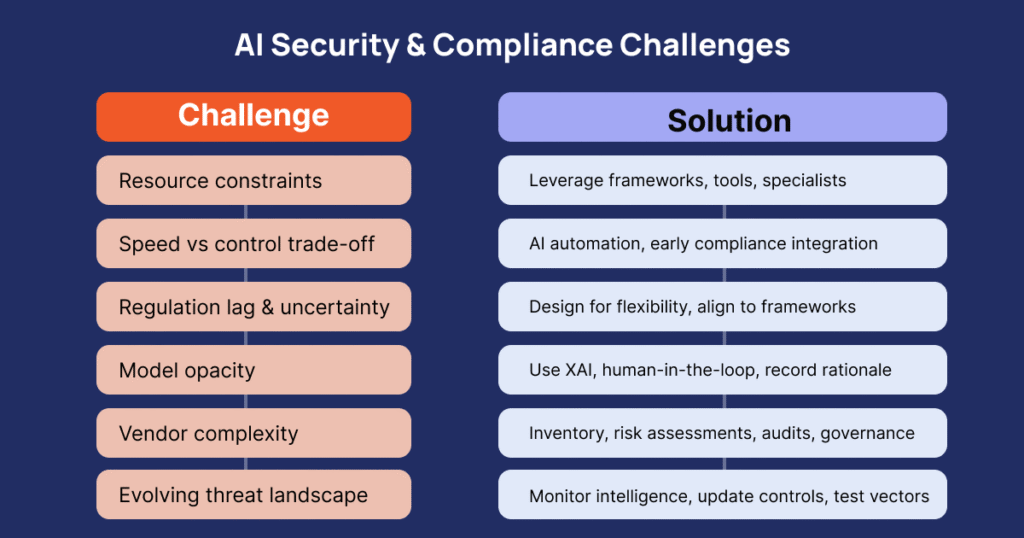
Challenges & How to Overcome Them
Despite the framework, many banks and service providers face real-world hurdles:
- Risk modeling enhancement: A European bank integrated AI models into its lending process, reducing credit loss provisions by 10%.
- Customer engagement: A leading U.S. bank applied an LLM strategy for personalized advisory, increasing cross-sell rates by 30%.
- Fraud prevention: An Asian institution deployed hybrid ML-LLM systems, cutting fraud detection times from hours to minutes.
These outcomes highlight that with disciplined execution, AI delivers measurable operational and financial gains — regardless of bank size or geography.
Conclusion
As the banking landscape evolves, AI implementation & strategy will define which players lead the industry. From AI roadmap planning to enterprise AI deployment, success depends on aligning data, technology, and people. Banks that build resilience through AI adoption, change management, and business process automation will achieve measurable growth.
In 2026 and beyond, banks that treat AI as a long-term digital transformation enabler will benefit from sustained efficiency gains, stronger customer relationships, smarter decision-making, and a future-ready competitive edge in an increasingly data-driven financial landscape.
PiTech Solutions supports regional and mid-tier banks in planning and implementing AI transformation initiatives that comply with banking regulations and ensure defense-grade protection.
Key Takeaways
- Connect AI to Business Goals: Every AI initiative should clearly tie to revenue growth, cost efficiency, or risk reduction — not technology exploration.
- Lay the Right Foundations:Unified data, scalable infrastructure, and seamless integration are non-negotiable for enterprise AI success.
- Prioritize Governance and Trust:Responsible AI requires transparent operations, regulatory compliance, and clear ownership of outcomes.
- Empower People: Equip employees with skills and clarity so they see AI as a productivity partner — not a threat.
- Scale with Structure: Use repeatable frameworks and centralized oversight to expand successful pilots across business units efficiently.
- Lead with Vision: Executive sponsorship and a clear roadmap turn experimentation into measurable enterprise transformation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do enterprises overcome resistance and manage change during large-scale AI rollouts?
Start by keeping people at the center. Explain why AI matters, not just how it works. Train teams early, highlight success stories, and make adoption rewarding. When employees see real benefits, change feels less like a threat and more like progress.
What does a practical, successful AI/LLM project deployment look like for non-tech-heavy sectors?
It’s all about starting small and scaling smart. Pick one problem with clear ROI — maybe automating compliance reports or enhancing customer service with LLMs. Once the pilot works, build on that success with strong governance and data practices.